Embark on a journey through Process Improvement for Operational Efficiency, where we explore how businesses can streamline operations for maximum productivity and success.
Discover the key strategies and tools that pave the way for operational excellence in today’s competitive landscape.
Process Improvement for Operational Efficiency
Process improvement in the context of operational efficiency refers to the systematic approach of identifying, analyzing, and enhancing existing processes within an organization to optimize performance, reduce waste, and increase productivity.
Importance of Continuous Process Improvement
Continuous process improvement plays a crucial role in enhancing operational efficiency by fostering a culture of innovation, identifying bottlenecks, reducing errors, and streamlining workflows. It ensures that organizations remain agile and competitive in today’s rapidly changing business landscape.
Examples of Successful Implementation
- Toyota: Through its renowned Toyota Production System (TPS), the automotive giant has revolutionized manufacturing processes by implementing lean principles to eliminate waste and improve efficiency.
- Amazon: The e-commerce giant has transformed the retail industry by continuously optimizing its fulfillment processes, utilizing automation, and leveraging data analytics to enhance operational efficiency.
- McDonald’s: With its efficient drive-thru operations and standardized processes, McDonald’s has set a benchmark in the fast-food industry for delivering consistent quality and speed to customers.
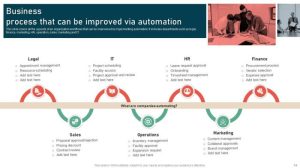
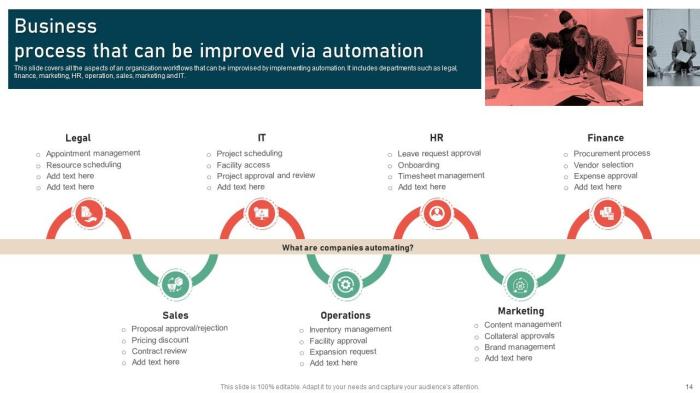
Identifying Inefficient Processes

Identifying inefficient processes within an organization is crucial for enhancing operational efficiency. By recognizing areas that are not performing optimally, companies can focus on making improvements that will lead to cost savings, increased productivity, and better overall performance.Data analysis plays a significant role in pinpointing areas for process improvement. Through the examination of key performance indicators, metrics, and other relevant data points, organizations can identify bottlenecks, redundancies, delays, or other inefficiencies that are hindering operations.
This data-driven approach provides valuable insights for decision-making and prioritizing improvement efforts.
Common Inefficiencies and Examples
- Overly Manual Processes: When tasks are predominantly manual and require excessive human intervention, it can slow down operations and increase the likelihood of errors. For instance, manual data entry processes can lead to inaccuracies, delays, and inefficiencies.
- Lack of Standardization: Inconsistencies in processes across different departments or teams can result in confusion, rework, and inefficiencies. For example, if each team has its own way of handling customer inquiries, it can lead to inconsistencies in responses and delays in resolving issues.
- Inefficient Communication Channels: Poor communication channels, such as reliance on emails for urgent matters or unclear communication protocols, can lead to misunderstandings, delays, and inefficiencies. For instance, if critical updates are buried in lengthy email threads, important information may be overlooked.
Implementing Process Improvement Strategies
Implementing process improvement strategies is crucial for enhancing operational efficiency in any organization. It involves a series of key steps that must be carefully planned and executed to ensure success.
Key Steps in Implementing Process Improvement Strategies
- Identify areas for improvement: Conduct a thorough analysis of existing processes to pinpoint inefficiencies and bottlenecks.
- Set clear objectives: Define specific goals and outcomes that you want to achieve through process improvement.
- Develop an action plan: Create a detailed plan outlining the steps to be taken, resources required, and timelines for implementation.
- Implement changes: Roll out the proposed improvements gradually, ensuring minimal disruption to ongoing operations.
- Monitor and evaluate: Continuously track the impact of the changes made and make adjustments as necessary to optimize results.
Importance of Employee Involvement and Feedback
Employee involvement is key to the success of process improvement initiatives. By actively engaging employees in the process, you can benefit from their invaluable insights and firsthand experience. Encouraging feedback from employees can help identify additional areas for improvement and promote a culture of continuous learning and innovation.
Tips for Creating a Culture of Continuous Improvement
- Encourage open communication: Foster a work environment where employees feel comfortable sharing their ideas and suggestions for improvement.
- Provide training and support: Invest in training programs to equip employees with the necessary skills and knowledge to drive process improvements.
- Recognize and reward success: Acknowledge and celebrate the achievements of individuals and teams who contribute to enhancing operational efficiency through process improvement.
- Lead by example: Demonstrate a commitment to continuous improvement at all levels of the organization, inspiring others to follow suit.
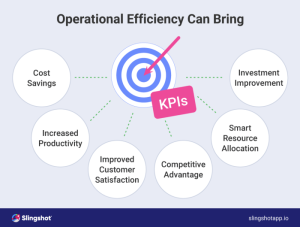
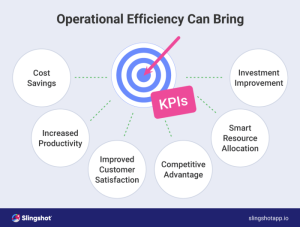
Measuring Operational Efficiency

Measuring operational efficiency is crucial for assessing the effectiveness of process improvement initiatives. By using specific metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs), organizations can track their progress and identify areas for further enhancement.
Different Metrics and KPIs
When measuring operational efficiency, organizations often rely on a variety of metrics and KPIs to gauge performance. Some common measures include:
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE): This metric calculates the performance of equipment in manufacturing processes, taking into account availability, performance, and quality.
- Throughput: This metric measures the rate at which products are produced or services are delivered within a specific timeframe.
- Cycle Time: This metric assesses the time it takes to complete a process or task from start to finish.
Setting Benchmarks and Goals
Setting benchmarks and goals is essential for measuring the success of process improvement efforts. By establishing clear targets, organizations can compare current performance against desired outcomes and track progress over time. This helps in identifying areas that require further optimization.
Tools and Software for Tracking Metrics
There are various tools and software available that can aid in tracking operational efficiency metrics. Some examples include:
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems: These systems help integrate and manage core business processes, providing real-time data for performance analysis.
- Business Intelligence (BI) tools: BI tools enable organizations to visualize and analyze data to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement.
- Performance Dashboards: Dashboards offer a visual representation of key metrics, allowing stakeholders to monitor performance at a glance.
In conclusion, Process Improvement for Operational Efficiency is not just a goal but a necessity for businesses looking to thrive in a fast-paced environment. Implementing these strategies can lead to tangible results and long-term success.
Questions and Answers
How can process improvement benefit operational efficiency?
Process improvement helps businesses identify and eliminate inefficiencies, leading to smoother operations and increased productivity.
What role does employee feedback play in process improvement?
Employee feedback is crucial for successful process improvement initiatives as it provides valuable insights from those directly involved in the processes.
How can businesses measure operational efficiency?
Businesses can measure operational efficiency using metrics like cycle time, throughput, and quality indicators to gauge performance and identify areas for improvement.